![]()
![]()
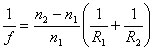
Go to lens equations.
Draw a suitable diagram for each problem. It may prove useful to have a copy of the lens sign
conventions nearby while attempting these problems
1. An object is located 40 cm to the left of a convex lens f = 30 cm. A second lens f = 20 cm is located 150 cm to the right of the first lens. Determine the nature, position, and relative size of the final image.
2. An object is located 40 cm to the left of a convex lens f = 30 cm. A second lens f = 20 cm is located 130 cm to the right of the first lens. Determine the nature, position, and relative size of the final image. (This application is the lens arrangement for a primitive microscope or Keplerian telescope.
3. An object is located 40 cm to the left of a convex lens f = 30 cm. A second lens f = 20 cm is located 100 cm to the right of the first lens. Determine the nature, position, and relative size of the final image. (This application is the lens arrangement for correcting farsightedness.)
4. An object is located 40 cm to the left of a convex lens f = 30 cm. A second lens f = -20 cm is located 100 cm to the right of the first lens. Determine the nature, position, and relative size of the final image. (This application is the lens arrangement for correcting nearsightedness.)
5. An object is located 60 cm to the left of a convex lens f = 30 cm. To the right of the lens 40 cm away is a concave mirror where f = 20 cm. Determine the nature, position, and relative size of all the images formed. This is a lens/mirror analogy of set 1, problem 2, and of set 3, problem 6.
6. 2-lens problems
http://www.phys.ufl.edu/~phy3054/light/lenscomb/pracprob/compound.cgi
hit the button several times to get a new problem
|
|
 |
This page was last modified by mgosselin on 10/08/2005