Derivation of the Gaussian
Mirror Formula
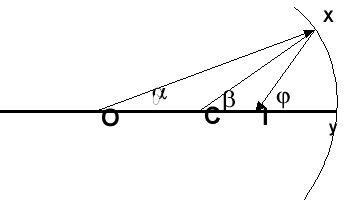 |
In the diagram at left, light leaves
the object at point O, strikes the mirror at point X, and crossses
t he principal axis at point I. A second ray leaves O, travels
along the principal axis, strikes the mirror normally, and converges
with the first ray at pt. I. It would be useful to be able to
predict where the imsage will be located .
|
|
In any triangle, an exterior angle is equal to the sum
of the two remote interior angles |
1 |
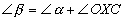 or or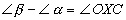 |
|
Same reason as step 1 |
2 |
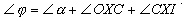 |
|
The second law of reflection |
3 |
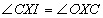 |
|
This is line 2 rearranged and XOC subbed for CXI |
4 |
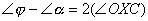 |
|
Sub line 1 into line 4 |
5 |
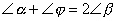 |
|
These are the measures of the three angles measured
in radians |
6 |
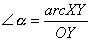 and and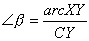 and and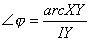 |
|
Subbing line 6 into line 7 |
7 |
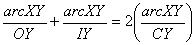 |
|
arc XY divides out |
8 |
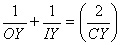 |
|
new definitions |
9 |
do = OY.......di= IY .....CY = R |
|
ta-dah! |
10 |
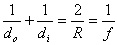 |
