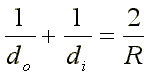
Do = DISTANCE FROM OBJECT TO MIRROR
Di = DISTANCE FROM IMAGE TO MIRROR
R = DISTANCE FROM CENTER OF CURVATURE TO MIRROR
f = FOCAL LENGTH = DISTANCE FROM PRINCIPAL
FOCUS TO MIRROR
|
|
 |
Object always to the left of mirror in single-mirror problems. Light travels left to right from object to mirror.
Object Distance
For most problems, Do is to the left of the mirror.
Do is positive if diverging rays strike the mirror. (Any single-mirror problem.)
Do is negative if converging rays strike the mirror. (Problem with lens & mirror.)
Image Distance
If Di is positive, image is real and is located to the left of the mirror.
If Di is negative, image is virtual and is located to the right of the mirror.
Radius of Curvature
If R is positive, mirror is concave. Center of curvature is located left of mirror.
If R is negative, mirror is convex. Center of curvature is located right of mirror.
If R approaches infinity, mirror is plane.
Image Formation - Real Images
-- only with concave mirrors
--only if Do > R/2
Magnification: M > 1 if object is between focal point and center of curvature.
M = 1 if object is at center of curvature
M < 1 if object is beyond center of curvature
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Image formation - Virtual Images
--Convex mirrors; any value of Do; |M| < 1
--Plane mirrors; any value of Do; |M| = 1
--Concave mirrors; Do < R/2 ; |M| > 1
This page was last modified by mgosselin on 10/08/2005